Abstract
Introduction
It is unclear whether evidence-based diagnostic protocols are followed when cancer patients are tested for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Evidence-based protocols reduce unnecessary diagnostic imaging, offer a patient-centered approach, and have the potential to standardize practice across medical specialties and settings. However, anecdote suggests that specialists who test people with cancer for VTE may prefer diagnostic imaging over clinical probability scoring and D-dimer testing. The aim of this study was to identify physician and patient knowledge, beliefs, values and preferences for VTE testing in cancer. This study was part of a program of research to set International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis standards for VTE testing in people with cancer.
Methods
This was an international qualitative interview study following COREQ guidelines. Semi-structured interviews with physicians and cancer patients were conducted via Zoom. We used purposive sampling to ensure inclusion of physicians from all specialties who test people with cancer for VTE, practicing across all continents. We invited people treated for cancer who had and did not have experience of VTE testing. We used grounded theory to create a conceptual framework which explains physician and patient values and preferences for VTE testing. Transcripts were coded by three researchers independently, who met to discuss their findings and agree on common codes. Researchers were a Thrombosis physician and two undergraduate students who ensured reflexivity was incorporated into their analysis.
Results
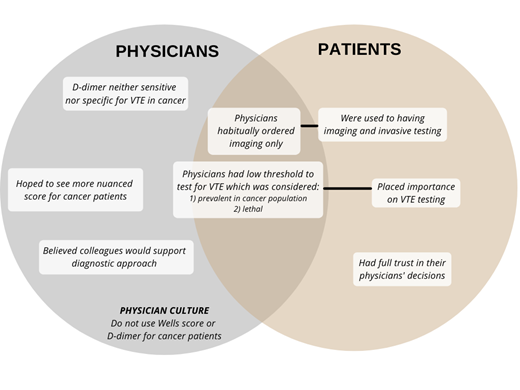
A total of 32 physicians and 6 cancer patients were invited to interview. Of those invited, 23 physicians and 6 patients across 6 continents completed an interview. Interviews lasted between 21 and 86 minutes. Our derived conceptual model can be seen in the attached Figure. Physicians reported a low threshold to test for VTE in people with cancer compared to those without cancer, because VTE was considered a fatal disease and highly prevalent in this patient population. Imaging was generally the only test used for VTE testing in cancer patients. Many participants relied on their Gestalt estimation of VTE probability when deciding whether to order imaging for pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis. Most thought that low Wells score in combination with a negative D-dimer was not sufficiently sensitive to exclude VTE and anticipated the Wells score and D-dimer to be elevated. The Wells scores had poor face validity because they do not include cancer-specific variables and participants hoped to see a more nuanced formal score for VTE testing in cancer patients. Participants believed that their colleagues would support their diagnostic approach.
Patients reported they were used to having tests and CT scans. Patients felt it was important for their physicians to prioritize testing for VTE. Patients had full trust and confidence in their physicians' testing decisions, particularly in decisions made by their oncologists.
Conclusion
Physicians have a low threshold to test people with cancer for VTE and tend not to use clinical probability assessment and D-dimer. Patients are comfortable having diagnostic imaging, feel VTE testing is important and have full trust in their physicians.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal